This post will cover all important queries of bloom taxonomy levels with example, bloom taxonomy verbs, Defining the bloom taxonomy of learning
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Learning was created in the 1950s by educational thinker Benjamin Bloom. The taxonomy, or levels of learning, distinguishes between cognitive (knowledge), emotional (attitudes), and psychomotor areas of learning (skills).
Read Also: What is a Problem-Based Learning Environment? Examples & Advantages
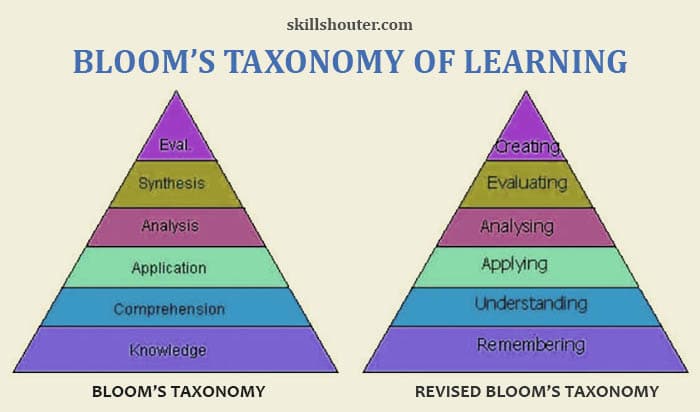
What are Bloom’s taxonomy levels (1956)?
The original Bloom’s Taxonomy framework consists of six levels that build off of each other as the learning experience progresses. It was developed in 1956 by Benjamin Bloom, an American educational psychologist. In 1956, Benjamin Bloom and his team of collaborators published their book, Taxonomy of Educational Objectives.
The followings are bloom taxonomy with an example of each level:
- Knowledge:
Identification and recall of course concepts learned - Comprehension:
Ability to grasp the meaning of the material - Application:
Demonstrating a grasp of the material at this level by solving problems and creating projects - Analysis:
Finding patterns and trends in the course material - Synthesis:
The combining of ideas or concepts to form a working theory - Evaluation:
Making judgments based on the information students have learned as well as their own insights
Bloom Taxonomy Pyramid
Revised Bloom’s taxonomy Levels (2001)
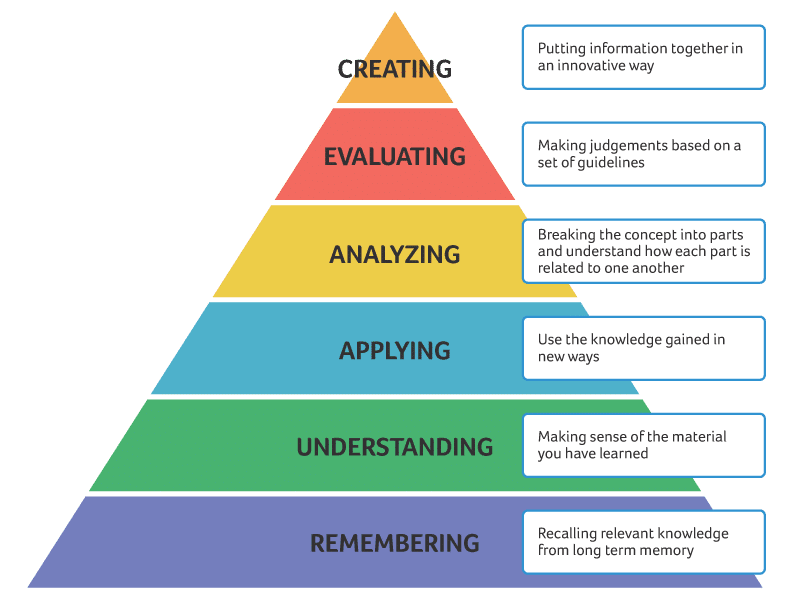
Bloom’s Taxonomy was amended in 2001 by a group of educational academics and cognitive psychologists to make it more action-oriented. Students complete a series of verbs in this manner to satisfy learning objectives. The levels of the revised Bloom’s Taxonomy are described below:
- Remember:
To bring an awareness of the concept to learners’ minds. - Understand:
To summarize or restate the information in a particular way. - Apply:
The ability to use learned material in new and concrete situations. - Analyze:
Understanding the underlying structure of knowledge to be able to distinguish between fact and opinion. - Evaluate:
Making judgments about the value of ideas, theories, items and materials. - Create:
Reorganizing concepts into new structures or patterns through generating, producing or planning.
Bloom Taxonomy Pyramid (Revised)
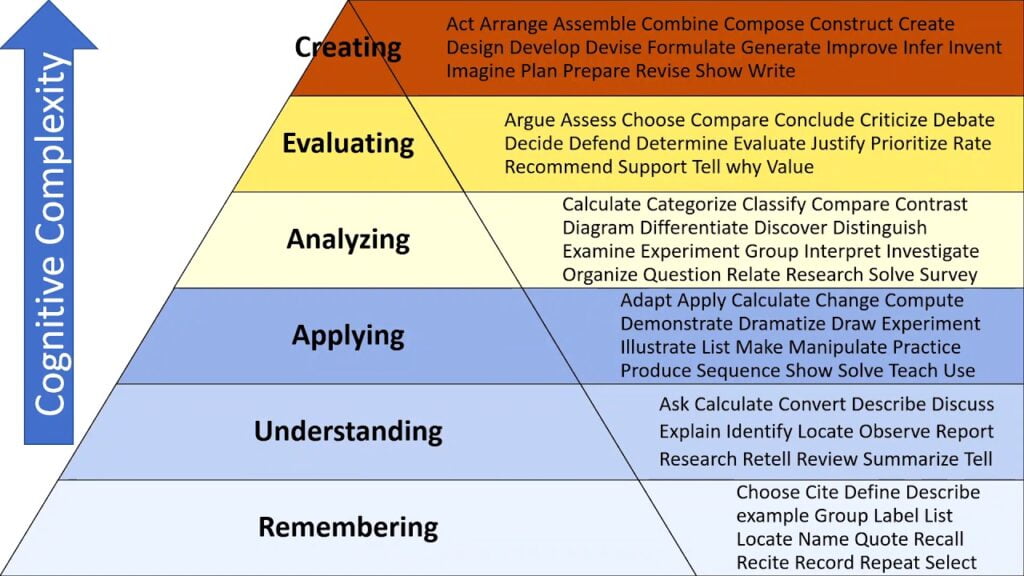
Bloom Taxonomy Chart
Bloom taxonomy example of verbs/words listed in the following chart:
| Remember | Understand | Apply | Analyze | Evaluate | Create |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cite | Add | Acquire | Analyze | Appraise | Abstract |
| Define | Approximate | Adapt | Audit | Assess | Animate |
| Describe | Articulate | Allocate | Blueprint | Compare | Arrange |
| Draw | Associate | Alphabetize | Breadboard | Conclude | Assemble |
| Enumerate | Characterize | Apply | Break down | Contrast | Budget |
| Identify | Clarify | Ascertain | Characterize | Counsel | Categorize |
| Index | Classify | Assign | Classify | Criticize | Code |
| Indicate | Compare | Attain | Compare | Critique | Combine |
| Label | Compute | Avoid | Confirm | Defend | Compile |
| List | Contrast | Back up | Contrast | Determine | Compose |
| Match | Convert | Calculate | Correlate | Discriminate | Construct |
| Meet | Defend | Capture | Detect | Estimate | Cope |
| Name | Describe | Change | Diagnose | Evaluate | Correspond |
| Outline | Detail | Classify | Diagram | Explain | Create |
| Point | Differentiate | Complete | Differentiate | Grade | Cultivate |
| Quote | Discuss | Compute | Discriminate | Hire | Debug |
| Read | Distinguish | Construct | Dissect | Interpret | Depict |
| Recall | Elaborate | Customize | Distinguish | Judge | Design |
| Recite | Estimate | Demonstrate | Document | Justify | Develop |
| Recognize | Example | Depreciate | Ensure | Measure | Devise |
| Record | Explain | Derive | Examine | Predict | Dictate |
| Repeat | Express | Determine | Explain | Prescribe | Enhance |
Blooms Taxonomy Questioning
Hers we are going to explain the examples of Bloom’s Taxonomy question stems and verbs list:
Level 1: KNOWLEDGE
Bloom taxonomy action verbs list:
· Describe
· Write
· Tell
· Relate
· Locate
· List
· Find
· State
· Name
Bloom taxonomy questions list:
· Describe what happened at…?
· How many…?
· Who was it that…?
· Can you name the…?
· What happened after…?
· Who spoke to…?
· Can you tell why…?
· Find the meaning of…?
· What is…?
· Which is true or false…?
Level 2: COMPREHENSION
SAMPLE VERBS
· Explain
· Interpret
· Outline
· Discuss
· Distinguish
· Predict
· Restate
· Translate
· Compare
· Describe
SAMPLE QUESTIONS
· Can you write in your own words…?
· Can you write a brief outline…?
· What do you think could of happened next…?
· Who do you think…?
· What was the main idea…?
· Who was the key character…?
· Can you distinguish between…?
· What differences exist between…?
· Can you provide an example of what you mean…?
· Can you provide a definition for…?
Level 3: APPLICATION
SAMPLE VERBS
· Solve
· Show
· Use
· Illustrate
· Construct
· Complete
· Examine
· Classify
SAMPLE QUESTIONS
· Do you know another instance where…?
· Could this have happened in…?
· Can you group by characteristics such as…?
· What factors would you change if…?
· Can you apply the method used to some experience of your own…?
· What questions would you ask of…?
· From the information given, can you develop a set of instructions about…?
· Would this information be useful if you had a …?
Level 4: ANALYSIS
SAMPLE VERBS
· Analyse
· Distinguish
· Examine
· Compare
· Contrast
· Investigate
· Categorise
· Identify
· Explain
· Separate
· Advertise
SAMPLE QUESTIONS
· Which events could have happened…?
· I … happened, what might the ending have been?
· How was this similar to…?
· What was the underlying theme of…?
· What do you see as other possible outcomes?
· Why did … changes occur?
· Can you compare your … with that presented in…?
· Can you explain what must have happened when…?
· How is … similar to …?
· What are some of the problems of…?
· Can you distinguish between…?
· What were some of the motives behind…?
· What was the turning point in the game?
· What was the problem with…?
Level 5: SYNTHESIS
SAMPLE VERBS:
· Create
· Invent
· Compose
· Predict
· Plan
· Construct
· Design
· Imagine
· Propose
· Devise
· Formulate
SAMPLE QUESTIONS:
· Can you design a … to …?
· Why not compose a song about…?
· Can you see a possible solution to…?
· If you had access to all resources how would you deal with…?
· Why don’t you devise your own way
· to deal with…?
· What would happen if…?
· How many ways can you…?
· Can you create new and unusual uses for…?
· Can you write a new recipe for a tasty dish?
· Can you develop a proposal which would…
Level 6: EVALUATION
SAMPLE VERBS:
· Judge
· Select
· Choose
· Decide
· Justify
· Debate
· Verify
· Argue
· Recommend
· Assess
· Discuss
· Rate
· Prioritise
· Determine
SAMPLE QUESTIONS:
· Is there a better solution to…
· Judge the value of…
· Can you defend your position about…?
· Do you think … is a good or a bad thing?
· How would you have handled…?
· What changes to … would you recommend?
· Do you believe?
· Are you a … person?
· How would you feel if…?
· How effective are…?
· What do you think about…?
See Also: Data Mining and Data Analysis Definitions and Differences
Udemy Teaching Training/Courses:
Outcome Based Education (OBE) & Academic Quality Assurance
The course covers fundamentals to advance level concepts and theories with plenty of practical examples and best practices as well as guidance on implementation. The course aims to make an ordinary teacher to an outstanding teacher.
What you’ll learn
- Breakthrough approaches to learning in education
- How to improve your teaching and learning potential
- Adopting student-centered learning techniques
- Different learning theories and taxonomies
- Academic Quality Assurance models and frameworks
- Implementation guidelines to better Quality Assurance in Education
Article by Navin